What Is an External Penetration Test?
Cyber threats are growing in number and sophistication, driving up the global cost of cybercrime each year. Statista estimates that by 2029, the financial impact of cybercrime will reach $15.63 trillion U.S. dollars. As businesses become more digital and interconnected, the potential for data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other malicious activities increases, increasing both economic and reputational risks. This rising trend highlights the importance of proactive cybersecurity strategies, such as external penetration testing.
This guide will explain exactly what external pen testing is, the methodology it follows, why it’s important, the benefits it can provide for your business, and how it differs from internal penetration tests.
External Penetration Testing Explained
An external penetration test, also known as an external pen test, is a security assessment that simulates how an external threat actor would attack an organization’s systems.
This test targets an organization’s perimeter systems. It focuses on external-facing assets such as public-facing websites, internet-accessible hosts, and web applications. If you can identify any security weaknesses and potential threats in these assets, you can improve your cyber defenses.
Cyber attack simulations are one of the main features of an external pen test. These can help your business identify the potential impact of a successful breach. This approach provides actionable feedback and remediation advice for improving overall security.
How External Penetration Testing Works
External penetration testing employs a systematic approach to imitate attacks, revealing potential weaknesses in network defenses and external applications. Here’s a closer look at the distinct features that make this type of testing indispensable:
Real-world attack simulation: This copies real-world attack scenarios that an attacker could use to gain unauthorized access from outside the organization. This helps identify weak points in network defenses and external applications.
Vulnerability assessment: Testers use a variety of tools and techniques to scan for vulnerabilities in public IPs and domain names. They test for common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and buffer overflows, which are typical entry points for hackers.
Remote testing: Unlike internal testing, external penetration tests are performed remotely, mimicking the actions of an actual attacker trying to infiltrate the organization’s systems from outside the network perimeter.
Detailed reporting: After the external pen test is complete, you’ll receive a detailed report that outlines discovered vulnerabilities, the severity of each issue, and recommendations for remediation to help you prioritize security enhancements.
Minimized disruption: Care is taken to ensure that external testing does not disrupt normal business operations or cause downtime, making it a non-intrusive yet effective method to strengthen external security defenses.
Different Types of Penetration Tests
To ensure your business is as protected as possible from cyber threats, there are a few types of penetration testing to choose from:
Black Box Testing
This type of external pentest replicates an attack from a hacker with no prior knowledge of the system’s architecture. The testers do not have access to any internal information of the targeted systems, much like a real external attacker.
White Box Testing
Assumes the attack is being carried out by someone with extensive knowledge of the system. The penetration tester has complete access to a comprehensive blueprint of the organization’s network infrastructure, source codes, IPs, and even the algorithms in use.
Gray-box testing
This is a blend of both black and white-box testing. The tester has partial access to the system’s internals, often mimicking the threat level of an external party that has gained significant, but not complete, system information.
These various methodologies are formulated to offer your organization a holistic understanding of your systems’ vulnerabilities. By selecting the most suitable method, you can focus on detailed areas of concern, improving security measures to safeguard against both known and unknown cyber threats and protect valuable data.
How Long Does an External Pen Test Take?
Typically, a basic external pen test ranges from a few days to a couple of weeks; however, the duration of an external network penetration test can vary significantly depending on several factors, such as:
- Complexity/size of the network
- Depth of the test required
- The specific goals set by the organization
For smaller networks with limited scopes, a test can be completed relatively quickly. In contrast, larger networks with more comprehensive testing requirements may require a more extended period to thoroughly examine all potential vulnerabilities. Additionally, the testing process can be extended if the security testing uncovers significant security issues that need deeper investigation.
You should also account for the time needed after testing to review the findings, implement remediation measures, and potentially retest the system to ensure all vulnerabilities have been adequately addressed.
External Penetration Testing vs Internal Pen Testing
There are two main types of pen tests: external and internal. Each serves a different purpose and focuses on different attack surfaces within an organisation’s network. Understanding the differences between external and internal pen testing is important to ensure you’re making the right decision for your business.
Feature | External Penetration Testing | Internal Penetration Testing |
Focus | External-facing assets: websites, apps, external network services | Internal network assuming insider threat or attacker access |
Purpose | Identify and fix vulnerabilities that are exploitable from the outside | Assess risks and potential damage from inside |
Methodology | In-depth, manual process by experienced testers | In-depth assessment of internal systems and controls |
Attack Simulation | Mimics external attacker actions to test access to sensitive data | Assesses lateral movement and insider threat scenarios |
Outcome | Shows how far an external attacker could penetrate; tests detection and response | Shows how far an internal attacker could move; tests internal controls and response |
Frequency | Typically sporadic for a realistic, detailed assessment | Typically conducted periodically, especially after changes to internal systems |
Resource Requirement | High: requires skilled testers and manual effort | High: requires skilled testers familiar with internal systems |
Perspective | Outside-in: protects against external threats | Inside-out: protects against internal threats |
External Penetration Testing or Vulnerability Scanning?
If you’re familiar with external vulnerability scanning, you may notice that external penetration testing has some similarities. Vulnerability assessments and penetration testing services tend to go hand-in-hand. While both external penetration testing and vulnerability scanning focus on securing your organisation’s external-facing systems, they serve different purposes and deliver different levels of insight.
Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning is an automated process that identifies known security weaknesses in systems. It provides a broad overview of potential vulnerabilities but does not simulate real-world attacks.
External Penetration Testing
External penetration testing, on the other hand, is a manual and in-depth assessment performed by cybersecurity professionals. It goes beyond simply identifying weaknesses by actively exploiting them to determine the potential impact on your organisation.
External Penetration Testing Methodology and Process
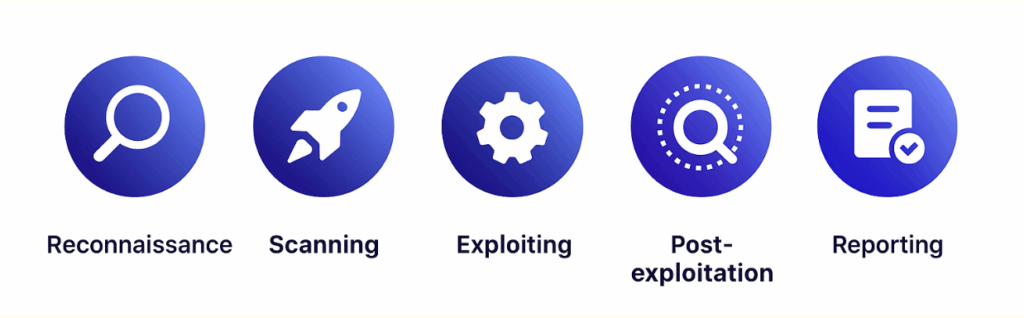
The process of external penetration testing is meticulously planned and follows a systematic approach. While there may be some variations in specific steps, a typical penetration test often includes the following stages:
1. Reconnaissance
This is the initial phase where the penetration tester, or pentester, gathers as much information as possible about the target network and systems. It could involve methods like port scans or checking public databases for any known vulnerabilities.
2. Scanning
Here, the pentester uses penetration testing tools like Nmap, Wireshark, Nessus, and Burp Suite to establish a detailed understanding of the organization’s system. These tools perform different tasks such as mapping out the network, identifying live hosts, or checking for open ports and services.
3. Exploiting
This is the stage where the actual attacking begins. The pentester uses the information collected in the scanning phase to exploit vulnerabilities using such tools as Metasploit. They attempt to gain access to the target system or network, mimicking the actions of a malicious attacker.
4. Post-exploitation
After gaining the required access, the penetration tester explores the network to find out what kind of valuable data or resources they can access and to what extent, simulating what a real attacker might do once they’ve breached the system.
5. Reporting
In this concluding stage, the pentester provides a comprehensive report detailing their findings, including the weaknesses identified, data that could be accessed, and necessary remediation advice.
Benefits of External Penetration Testing
External penetration testing offers numerous tangible benefits to your business, shaping a sturdy foundation for your cybersecurity framework. Some of the reasons why businesses use external pentests are to:
Identify Vulnerabilities
Allowing you to focus on the highest risks that matter to your business through asset classification, risk prioritisation, and remediation.
Mitigate Risks
External pentesting gives your business insight into the potential impact of an attack. That helps you prioritize risks and allocate resources intelligently to enhance your cybersecurity.
Comply with Regulations
Certain industries need regular pentesting for regulatory compliance. If you maintain this compliance, it protects you from legal penalties and improves your reputation.
Save Money
Data breaches can be expensive, leading to halted operations and fines for losing customer data. Identifying vulnerabilities early helps prevent these costs.
Manage Vendors
External penetration tests provide a comprehensive view of your cybersecurity, including third-party service security, and reveal if vendors introduce vulnerabilities.
External Penetration Testing Checklist
A checklist for external penetration testing is crucial for thoroughly evaluating an organization’s cybersecurity defenses, ensuring effective preparation, execution, and follow-up.
- Define scope: Identify which systems, networks, and applications will be tested.
- Gather intelligence: Collect data about the target environment to plan the attack vectors.
- Testing tools preparation: Choose appropriate tools and techniques based on the scope and intelligence gathered.
- Conduct testing: Execute the penetration test, documenting all steps and findings.
- Analyze findings: Assess the vulnerabilities exploited and the data accessed.
- Report and remediate: Provide detailed findings and recommend security enhancements.
- Review and retest: Verify that security improvements have been implemented effectively.
Considerations for Choosing an External Penetration Testing Provider
While we now understand why external penetration testing is so important for businesses, here are some key points you should consider when choosing your provider:
Define Requirements
Define the scope of work by specifying what needs testing (networks, applications, systems) and determine your objectives for the test (identify vulnerabilities, ensure compliance).
Evaluate Expertise
Select providers with certifications (OSCP, CISSP, CEH), industry experience, regulatory knowledge, and successful case studies or references.
Understand Approach
Evaluate penetration testing providers by their methodologies (OWASP, NIST, PTES), use of automated and manual tools, and clear, actionable reports.
Consider Compliance
Verify that their services comply with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS). Ensure they have strong confidentiality agreements and data protection measures in place.
Support
Evaluate their ability to communicate findings and recommendations effectively. Check if they offer ongoing support and re-testing to verify remediation of vulnerabilities.
Cost and value
Understand their pricing model and ensure it fits within your budget. Assess the value provided for the cost, considering the quality of their services, expertise, and support.
Reputation & Reviews
Research their reputation in the industry through reviews, testimonials, and industry forums. Check if they have received any industry awards or recognitions.
Trial Engagement
If possible, start with a smaller pilot project to evaluate their capabilities and work style before committing to a larger engagement.
Why Choose Rootshell for External Penetration Testing Services?
External penetration testing is an investment that your business must make to protect against cyber threats. It removes any guesswork from your defense strategy, so your cybersecurity is as airtight as it can be.
Rootshell delivers more than a point-in-time test, we provide continuous visibility of your external attack surface. Our expert red teams combine leading tooling with real-world adversarial tactics to uncover the vulnerabilities that matter most.
Every finding is delivered through the Rootshell Platform, giving you clear remediation guidance, daily exploit intelligence, and prioritised workflows to fix risks faster. With Rootshell, you get proactive defence, measurable improvement, and a security partner committed to keeping you ahead of emerging threats.
Book your Demo to get started with your external security testing today.


