Vulnerability management is an important part of any cybersecurity strategy. However, for larger organizations, the complexity of your systems and the sheer number of vulnerabilities can pose a major challenge. Resource-intensive manual approaches won’t be up to the task; instead, you need an automated vulnerability management solution.
Automating vulnerability management is essential for staying on top of remediation deadlines. A 2024 report by Bitsight revealed that over 60% of known exploited vulnerabilities were not fixed past their deadlines, with vulnerabilities taking an average of 137 days (4.5 months) to resolve. Automation helps cut this delay significantly, reducing risk exposure and keeping organisations compliant.
In this post, we’ll explain why automating your vulnerability management is an important step to upgrading your cybersecurity efforts. We’ll take you step-by-step through how to implement it effectively and the best practices you need to adopt.
What is Automated Vulnerability Management?
A business’s network and systems are always under threat from threat actors. The issue is that even small and medium-sized businesses are not safe. In fact, they might be targeted more since the assumption is that they won’t have a strict cybersecurity protocol in place.
When hackers attack a business, they look for exploitable weaknesses. Vulnerability management is the process of identifying security weaknesses in each one so you can reduce the attack surface. Once the vulnerabilities have been identified, steps can be taken to fix them.
Managing vulnerabilities is more than just the process of finding weaknesses. It is the end-to-end process of identifying, evaluating, prioritizing, and dealing with the flaws in the system.
Automated vulnerability management continuously identifies, assesses and remediates potential security issues with minimal human input. As a result, it ensures that the identification and classification of vulnerabilities are not only consistent but also substantially quicker.
Components of Automated Vulnerability Management
Automated vulnerability management incorporates the following elements:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Automated vulnerability scanning tools work tirelessly, scanning web applications, and systems to detect potential weak points.
- Vulnerability Data Analysis: Post-scan, these vulnerability scanners aggregate data, ensuring security teams have actionable intelligence at their fingertips.
- Patch Management: Automation aids in identifying necessary patches, further expediting the vulnerability remediation process.
- Continuous Monitoring: The dynamic nature of today’s digital environment means new vulnerabilities can emerge overnight.
Common Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities can be due to improper setup of software or hardware. They can also be created when a new feature is introduced or when you update an old piece of code. However, any exploitable attribute in your system can be considered a vulnerability.
Some common vulnerabilities are:
- Outdated software that has not been patched
- Zero-day vulnerabilities
- Misconfigurations in security
- Unsecured APIs
- Broken authentication
- SQL injection
- Weak user credentials
The Vulnerability Management Process
Managing vulnerabilities in your systems, as we discussed earlier, is more than just finding weaknesses. Here is how the vulnerability management process works:
Identification
The first step in the process is identifying the vulnerabilities that are present in your system. With an automated vulnerability management system, you have a scanner that goes through endpoints, networks, assets, and systems to find weaknesses that could be exploited.
Otherwise, the process is conducted manually, starting with checking with your employees to see if they’ve discovered any problems. Then, any systems or programs that have network access are scanned, and any services that run on the network are tracked.
Analysis
Once weaknesses are identified, they are assessed to find out how much time, money, and resources you’d need to spend to fix them. During this process, each vulnerability is assigned a Vulnerability Priority Rating (VPR) or a Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which is a rank based on:
- How easy it is for a hacker to exploit this weakness
- How much of a threat it poses to the network and business assets
- How long will it take to fix the weakness
This ranking enables you to prioritize the found vulnerabilities, so you can allocate resources efficiently and get the best results.
Treatment
Depending on the previous step, you can strategize your plan of action to deal with the identified vulnerabilities. Security weaknesses with a higher VPR are addressed first, and the idea is to remediate, mitigate, or accept the vulnerability.
Remediation: Resolve the vulnerability so it’s no longer a threat.
Mitigation: If the vulnerability cannot be resolved completely, steps should be taken to mitigate the impact it could have on the business.
Acceptance: If the vulnerability is low-risk and the cost of fixing it is higher than its potential risk, it is better to simply accept it whilst being aware of its existence.
Continued Reporting and Monitoring
Threats can constantly arise, meaning that you should assess your systems and vulnerabilities periodically. This allows you to keep up with the latest threats and keep your business safe.
Further, vulnerability management tools can assess, prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities at pace. This helps you minimize the risk of a successful attack and contributes to meeting your vulnerability management SLAs.
Types of Automated Vulnerability Scanning
- Network Vulnerability Scanners: Aimed at identifying vulnerabilities within the organization’s network.
- Cloud Vulnerability Scanners: Aimed at identifying vulnerabilities within an organization’s cloud infrastructure.
- Web Application Scanners: Focus exclusively on web applications, identifying potential weak points that might be exploited.
- Database Scanners: Designed to find vulnerabilities within an organization’s database.
- Wireless Scanners: Focus on potential vulnerabilities within wireless networks.
How to Automate Your Vulnerability Management Processes
1. Evaluate Your Requirements
If you are looking to automate your vulnerability management program, there are a few things you need to consider before you begin:
- The size and complexity of your IT infrastructure. The more complex your IT infrastructure, the more difficult it will be to automate vulnerability management. This is because you will need to have a tool that can scan a wide range of assets and identify vulnerabilities in a variety of operating systems and applications.
- The maturity of your cybersecurity program. If your cybersecurity program is not mature, you may need to start with manual vulnerability management before you can automate the process. This is because you will need to have a good understanding of your vulnerabilities and how to prioritize them before you can automate the remediation process.
- The budget you have available. Tools can be expensive, so you need to make sure you have the budget to implement them. You also need to factor in the cost of training your staff on how to use the tool and the ongoing costs of maintaining it.
If you take these factors into account at the planning stage, you’ll be able to identify the appropriate scope for your automation project. As a result, you’ll be better placed to allocate the right resources to design and implement it effectively.
2. Choose the Right Tool
Once you have considered these factors, you can start to look for an automated vulnerability management tool. When choosing a tool, you need to consider the following factors:
- The features and functionality of the tool.
- The ease of use of the tool.
- The support offered by the vendor.
- The cost of the tool.
When evaluating these factors, you should refer back to the requirements you established in the first stage. For instance, your budget and the complexity of your infrastructure will determine which tool is the right fit for your needs.
3. Implement Effectively
Once you have chosen a tool, you need to implement it in your environment. This process will vary depending on the tool you choose, but it typically involves the following steps:
- Installing the tool on your network.
- Configuring the tool to scan your assets.
- Scheduling the tool to run scans on a regular basis.
- Reviewing the scan results and taking action to remediate vulnerabilities.
The implementation of a new tool is not always straightforward, so we’ve outlined some best practices to help you below.
5 Best Practices for Automated Vulnerability Management
- Implement risk-based vulnerability management. Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their potential impact will help you focus on the most significant issues and avoid dedicating resources to fixing vulnerabilities that don’t pose a real-world threat to your organization.
- Integrate with your existing tools. Ensure your vulnerability management system seamlessly integrates with other tools in your security stack. This will limit the amount of manual intervention needed and ensure your vulnerability management process meshes with your other cybersecurity efforts.
- Regularly update scanners. Your vulnerability scanning tools need to be kept up-to-date in order to detect the latest vulnerabilities. Ideally, you should incorporate data from your threat intelligence feeds to stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Set up alerts and notifications. Your automated vulnerability management system should notify you of new vulnerabilities as soon as they are discovered. This will help you to take action to remediate them quickly and prevent them from being exploited by attackers.
- Review and refine. Vulnerability management is an ongoing process. You’ll need to regularly review your approach to ensure it aligns with the changing cybersecurity landscape and incorporates new technologies such as AI and machine learning.
- Implement risk-based vulnerability management. Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their potential impact will help you focus on the most significant issues and avoid dedicating resources to fixing vulnerabilities that don’t pose a real-world threat to your organization.
Benefits of Automated Vulnerability Management
Proactive Cybersecurity Protection
Rather than reacting to a breach after it happens, continuous vulnerability management helps you stay one step ahead of potential threats. Continuously monitoring your systems for weaknesses means that you can identify and address risks before they are exploited, protecting your data and maintaining business continuity.
Better Response Time
MTTD (Mean Time to Detect) measures how quickly a vulnerability is identified, while MTTR Mean Time to Respond tracks how fast it is fixed.
Automating vulnerability management shortens both by continuously scanning for weaknesses, rather than discovering them after an attack happens.
Vulnerability management tools can assess, prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities at pace. This helps you reduce the risk of a successful attack and contributes to meeting your vulnerability management SLAs.
Helps Improve Resources
Automating repetitive tasks like vulnerability scanning frees your IT team to focus on higher-value activities. While AI handles the routine identification of weaknesses, your experts can concentrate on fixing issues.
Automated scan reports assign priority scores to detected vulnerabilities, ensuring your team focuses on the most important risks first. Not all vulnerabilities carry the same threat, so prioritisation allows you to fix high-risk issues while categorising lower-risk vulnerabilities.
Reduces Human Error
Vulnerability management automation may list false positives that you then have to manually review. However, when traditional vulnerability management is done manually, it’s susceptible to human error.
Analysts are only human; things can slip through the cracks, be forgotten, or missed.
As we saw earlier, it’s sometimes necessary to accept that vulnerability can’t be fixed. However, that’s only acceptable when you are aware of the security flaw and know it does not pose a significant risk.
When you automate your vulnerability management, any weaknesses left on your systems are by design rather than human error.
Challenges of Automating Vulnerability Management
While the benefits of automated vulnerability management are extensive, they don’t come without challenges. You’ll need to consider the following:
- Upfront investment. Automating your processes will require an initial investment of time and money as you adapt your systems and secure the necessary tools.
- Training your teams. While automated vulnerability management requires less manual input, your teams will still need to learn how to manage the process effectively. You may need to provide formal training and increased oversight to avoid security lapses while they adapt.
- Managing false positives. Automated processes are more likely to identify apparent vulnerabilities that do not actually pose a threat. You will need to put verification processes in place to avoid spending resources fixing non-existent issues.
- Limiting downtime. Without proper scheduling, automated scanning can impact your systems, causing slowdowns that can impede service delivery.
These challenges can limit the effectiveness of your automated vulnerability management efforts, leading to unforeseen disruption or unexpected costs. However, with proper preparation and the right vulnerability management solution, these can be mitigated.
Automated Vulnerability Management with Rootshell Security
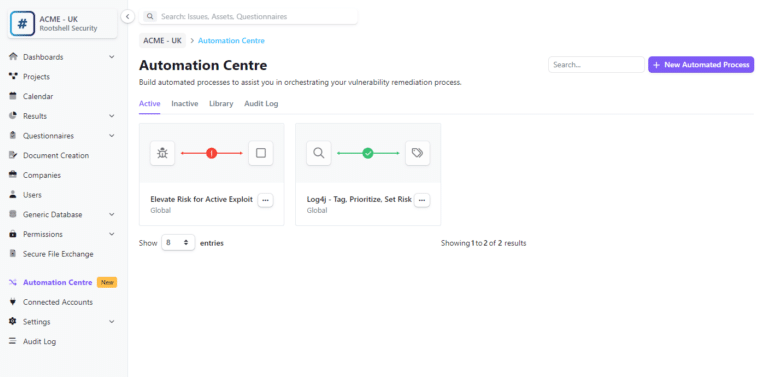
The Rootshell Platform is a vendor-agnostic vulnerability management solution that centralizes results from vulnerability scans and other security assessments, including penetration testing.
Our Automation Centre helps organizations receive, triage, and remediate vulnerabilities faster than ever. With powerful triggers and customizable rule sets, teams can prioritize and manage vulnerabilities. Rules can automatically assign issues to the right colleague or team based on factors like priority status, meaning that the most urgent vulnerabilities are addressed immediately.
Take control of your cybersecurity with Rootshell Security. Get in touch today to arrange a fully personalized guided demo with one of our experts.


